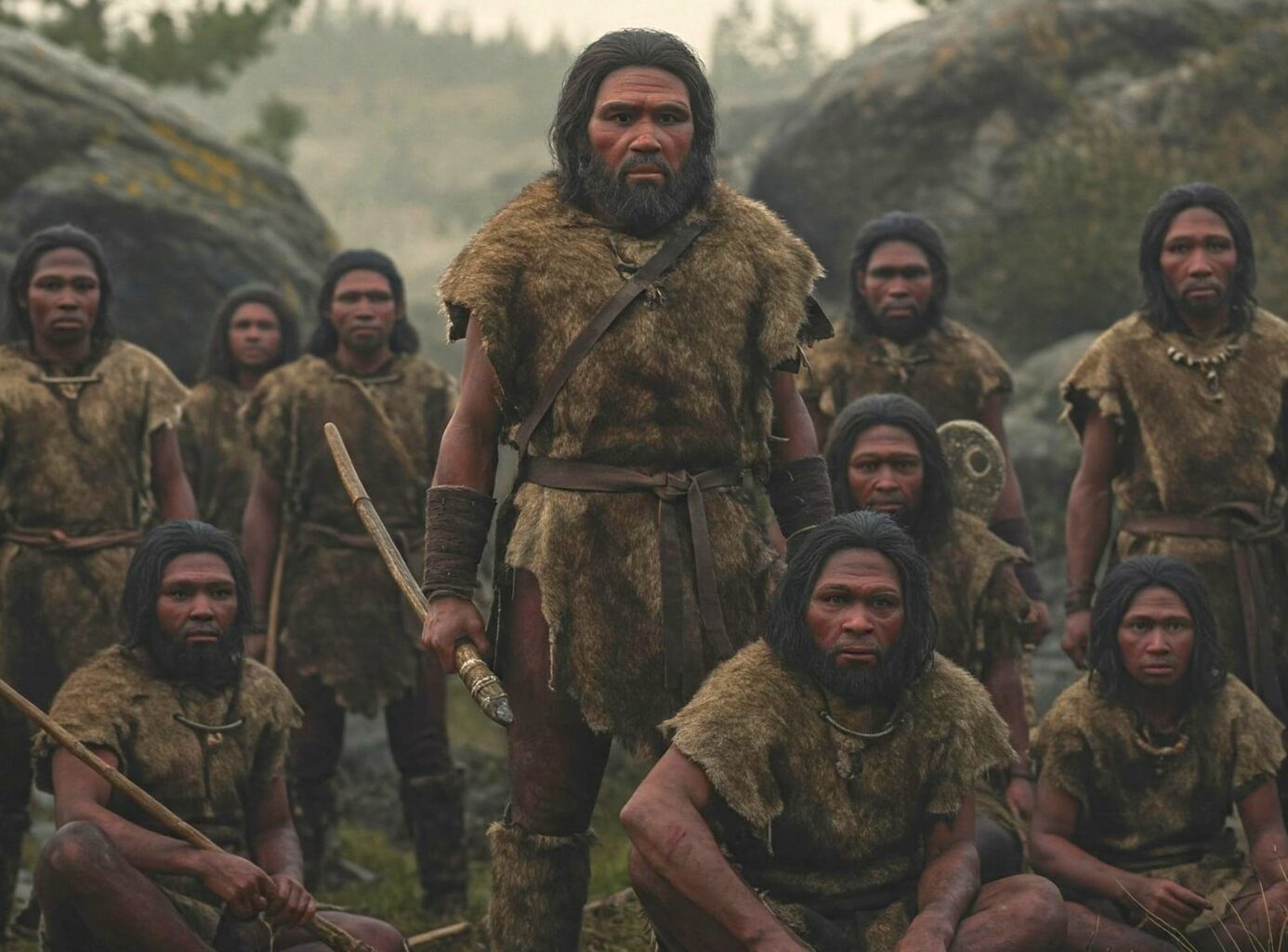
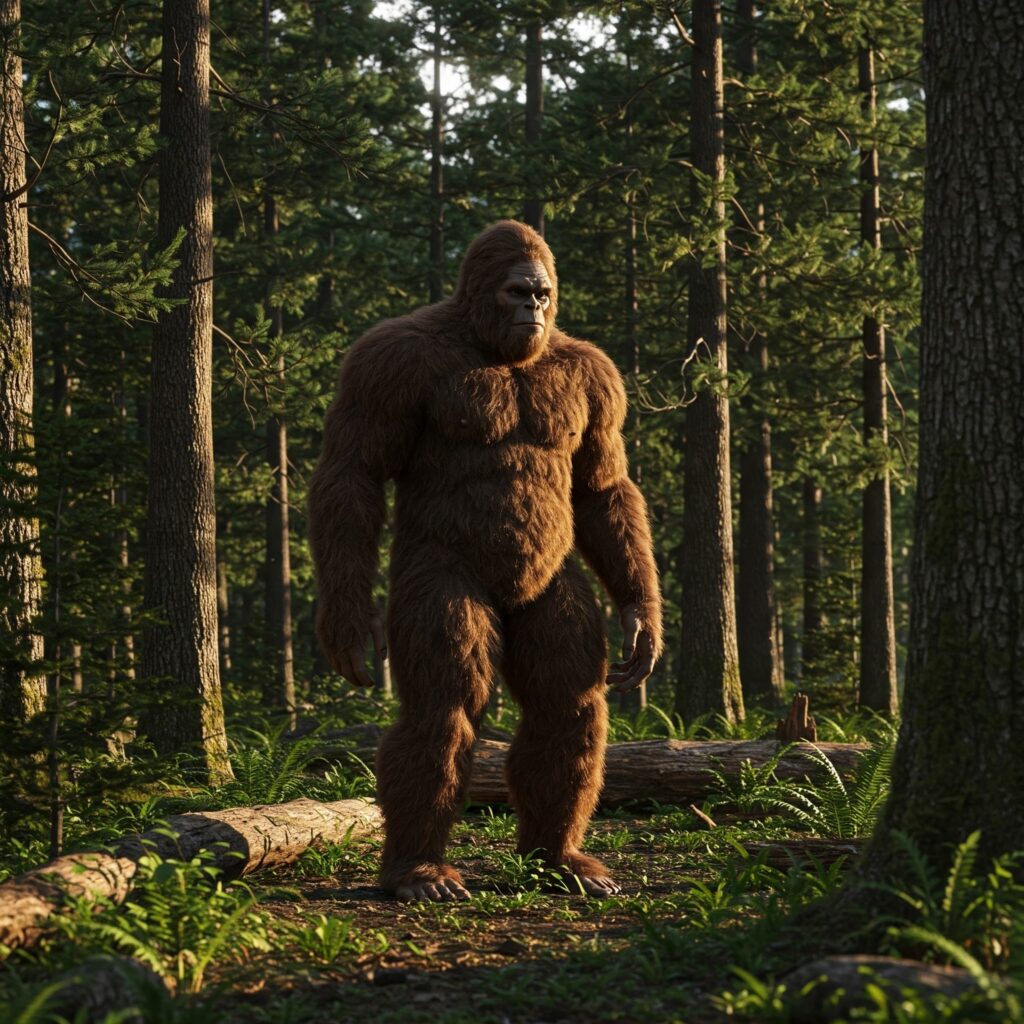
We are all familiar about the creatures called Bigfoot or Sasquatch that live in the vast wilderness of North America-the United States of America and Canada. Bigfoot or Sasquatch have been called “early man” or “early humans”, but these creatures are very tall, extremely hairy, have long arms that reach almost completely down to their legs, little or no neck, and look very ape like except many of these animals have a somewhat human looking face, while others look like a very huge gorilla. There is enough circumstantial evidence for the existence of these sub human life forms. There thousands and thousands of eye witness testimonies, footprints and plaster casts of footprints that show intricate physiology of a strange being weighing many hundreds of pounds, and hair samples biologists have discovered that come from an unknown primate.
There are lots of photographs and a small number of videos, even though these pictorial things are controversial. But, what about very ancient humans that go back through time 50,000 years, 100,000 years, 200,000 years, 300, 000, and 1,000,000,000 years or even more still living secretly in vast wilderness areas where there are caves, rivers, plenty of animals and fish, and various rocky areas? Very ancient humans, still breeding, that do not look like a bigfoot? In North America, there are vast forests, if explorers and hunters happened to see the living descendants of these very prehistoric humans in forests, such modern people would not mistake them for a sasquatch but would only see human beings. But some of the other groups of very ancient humans, as the Neanderthals, the average modern humans of today would not see any real pronounced odd features, but highly trained anthropologists would soon see the somewhat slight different indications. Also, no-one very deep in a forest would except see a living, very ancient species of humans, but would expect see a bigfoot.
Only the very oldest group of prehistoric humans called homo habilis, who lived 2.3 million years ago to 1.8 million years ago, would ordinary modern people recognize as very strange since homo habilis, even though looking almost human, would have certain apeish features in the face around the eyes, nose, and mouth and have more bodily hair than humans of today. Homo Habilis actually belong to the most human looking of the bigfoot; sasquatch series. The most ape looking bigfoot-sasquatch in recent times would be the Ramapithecus Blacki, who lived about 14 million years ago to about 215,000 years ago and looked like a real giant sized gorilla.

Now, here is a very important point to consider, since bigfoots crossed over to the Americas, shortly after the Ice Age when the continents were joined together by the Beiring Straight, as other animals did so as mammoths, bison, tigers, lions, moose, elk, brown bears, back bears, wolves, and early humans would have crossed over as well. And there were other animals as horses, camels, caribou, and some back bears that went the other way; migrating out of the Americas over the land “bridge”. While anthropologists admit that early humans did come to American back then, these anthropologists believe only homo sapiens came over then. Those ancient homo sapiens look exactly as people do today. But, what if early humans came over as well, humans as the Cro-Magnons, the earlier Neanderthals, and the still earlier Homo Heidelbergensis, and the more earlier Homo Erectus; from the later period; all 4 human groups that look like modern humans do except to the highly trained eyes of scientists?
The Cro-Magnon man, who did have a fully developed language, were anatomically similar to current day Europeans, West Africans, and North Africans, but they were more robust,having larger brains, broader faces, more prominent bow ridges, and bigger teeth compared to completely modern people. The earliest known remains of the Cro-Magnons are radio carbon dated to 46,000 years before present to 43,000 years before present and found in Bulgaria, Italy, and Great Britain. Cro-Magnons are actually the same basic species of current day Homo Sapiens.
Anthropologists will tell you early humans came into the Americas from about 29,000 years ago to about 16,000 years ago, Some scientific researchers place the number at 15,000 years in the past, others will put the umber as low as less than 13,000 year, even though there is plenty of circumstantial evidence to show a much. much older timeline. Evidence suggests humans must have been in the Americas as early as 30,000 years ago, supported by archeological discoveries like stone tools and fossilized human footprints in sites like the Chiquihutte Cave in Mexico and White Sands National Park in New Mexico. Other anthropologists will tell you from about 33,500 years ago to 30,000 years back. However,a group of scientists, since 2017, believe that a group of humans occupied what is now the USA state of California approximately 130,000 years ago. And that Neanderthals and maybe an earlier species of humans lived in California at that time.
In the journal from The United Kingdom called “Nature”, an article dated April 26,2017 was published and it gives a detailed report that some 130,000 years ago,human beings existed in California,because of certain mastodon bones and large stones seemingly used as tools found at the Cerutti Mastodon site near the city of San Diego in San Diego County, which was unearthed in 1992 during a highway expansion project. Steven Holen, a doctor of Philosophy and of Anthropology of the University of Kansas and Thomas Deme’re’, a doctor of Philosophy and Paleontology from the University of California,Los Angeles, and theorized that these bones show signs of human activity including being broken and used for marrow extraction or tool creation, and that the site is the oldest known archeological site in North America. While skeptics argue that the mastodon bones breakage could have been caused by just natural activity, the two scientists disagree. The research site involved a team of scientists from the USA and Australia. The archeological site was dated using a uranium=series of disequilibrium methods that indicated a burial date of 30.7+ or 19.4 thousand years ago, suggesting the fossils were stillfresh when broken down with the rocks used as tools.
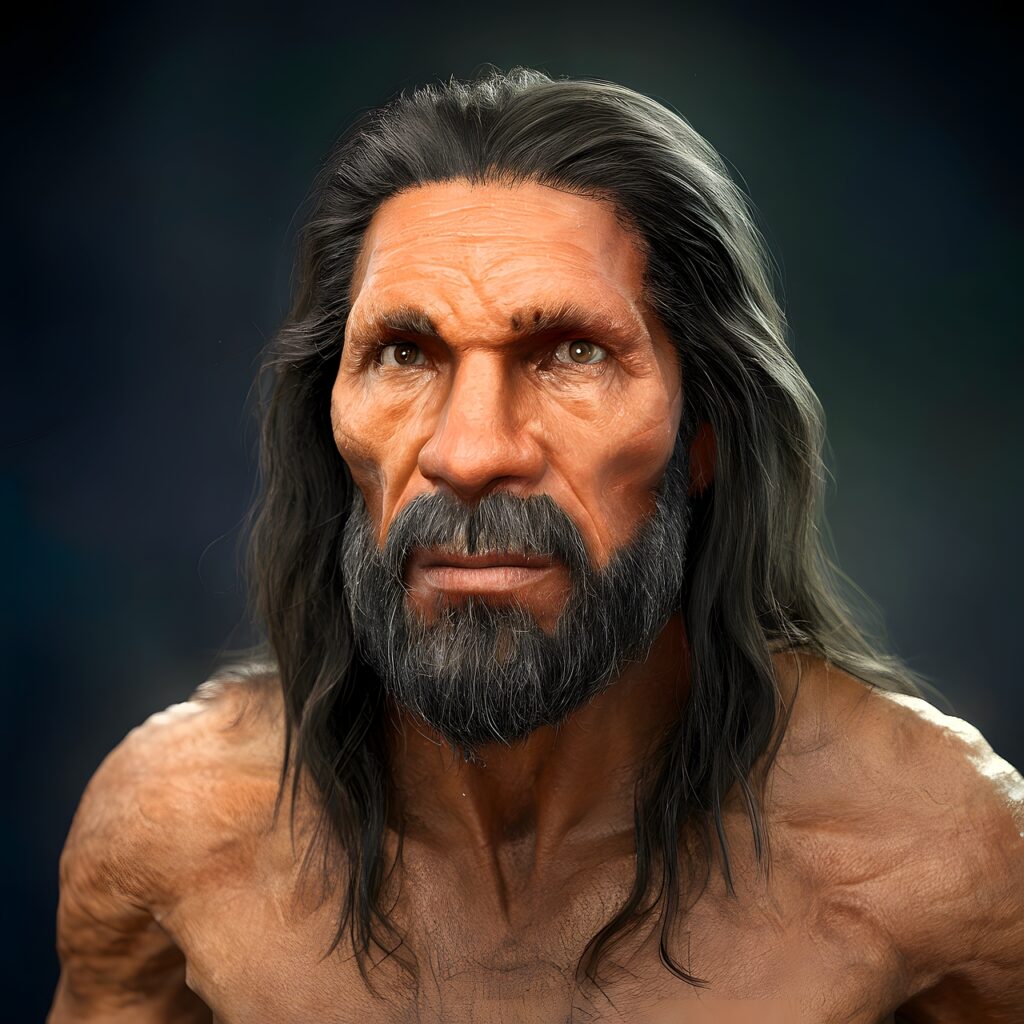

A group of paleontologists from the Natural History Museum of San Diego spent the next five months excavating the sediment the bones and stones were found. The scientists discovered more strewn about bone fragments that all appeared to come from a single mastodon,which from the start of the discovery of the bone pieces, seemed strange. The thick bones were broken and smashed. Near the butchered animal lie five big stones circular in form.
In an experiment to see what bones would look under human activity, fresh elephant bones in Tanzania were broken apart, and these bones fractured at the same angles and remains scattered in the same manner compared to the found mastodon bones. Doctor Deme’re’ and his band of scientists rejected the idea that predators were responsible regarding the mastodon bone breakage.
Doctor Deme’re’ said: “It is hard to envision a carnivore strong enough to break a mastodon leg bone”. On the archeological site, the team discovered small chips fit very well into the rocks that strongly inferred that such particles broke off while the rocks were used as hammers. Also, the scientists found scratches on the mastodon fossils and the rocks used to smash the elephant bones also had scratches.
The bones and rocks were lying upon a sandy flood plain by a meandering stream and therefore these relics could have to have been collected together from a violent stream; the human hunter=gatherers must have brought these rocks to the mastodon. The early humans seemed to have been trying to get the marrow out of the bones to ear while using the bone fragments to fashion tools. In much older sites in different parts of the world, there is evidence of such human activity.
Neanderthals were a group of humans known to live in Eurasia between roughly 400,000 and 40,000 years ago. Though the Neanderthals looked a very great deal human, they exhibit a longer, lower skull and a wider pelvis. Even the three tiny bones in our middle ear, necessary in hearing are quickly discerned as different from those early human ancestors, with careful measurement. Neanderthals could talk and even possessed a highly developed language; apparently basically fully “modern style” speech.
Anatomic evidence for a language: strong similarity between modern humans regarding the hyold bone, a small u-shaped bone in the back of the throat that connects to the larynx; vocal tracts and auditory pathways extremely similar to current humans; the same hearing range of today’s humans including the higher frequencies associated with modern human speech sounds.plus other research evidence published in scientific journals.
Furthermore,there were Neanderthals who were superb artists that produced colorful,detailed, realistic pictures of animals on the walls and ceilings of caves in various places still surviving in Europe. And beautiful jewelry was produced by these early humans and various skilled stone tools and projectiles.
The first almost truly looking modern humans,as distinguished from the partly apeish looking humans, is Homo Erectus that had a robust build with long arms relative to the torso,a skull with a prominent brow ridge, a sloping forehead, and a reduced chin. Homo Erectus lived around 1.9 million years ago to approximately 110,000 years ago. Some of the later types of Homo Erectus looked more human in the face than the much earlier types of this species did. Also, there is a belief among scientists that Homo Erectus could talk; these early humans had some sort of a language; perhaps a “proto language”or a rudimentary form of communication, rather than the complex language we use today and these prehistoric humans used gestures, sounds, and simple vocializations when communicating. Their hyoid bone,though identical in shape to that of modern humans, lacked the muscle impressions, and has a shield-shaped body which suggests they may not have the anatomical requirements for modern human level speech. While we have no direct proof that Homo Erectus could talk, it is believed they could because of their advanced cognitive abilities, tool use, storing provisions,planning crossings, and the potential for symbolic behavior that suggest a requirement for intricate communication. Also, there is evidence of these early people being sailors, that they were able to construct seagoing vessels,and must have used language to successfully sail. Furthermore, Homo Erectus was advanced enough to have controlled use of fire since “microscopic traces of wood ash” have been discovered at their sites roughly a million years ago.
In the Americas, Native American Indians, from ancient times to even the late 1800s, have been well aware of strange peoples that spoke different languages living in remote wilderness areas, especially high up in mountain ranges that some of these other peoples lived far apart from each other in very primitive conditions without artwork,but they cooked their meats with fire, and simply wore animal skins in the cold weather. At times, these very early humans men were described as being very muscular, with great strength, and excessively hairy. Settlers from Europe and Asia to the Americas in pioneer times noticed such substandard, even backward or primitive peoples as well.
Since the vast wilderness areas of the world today can hide the creatures known as bigfoot or sasquatch, why cannot the great wilderness places of the world today hide prehistoric human peoples too?